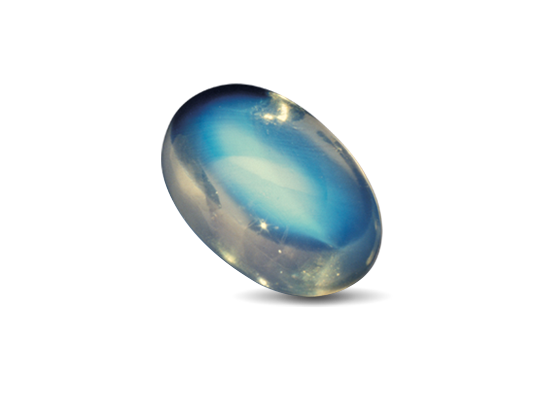
Overview
About Moonstone

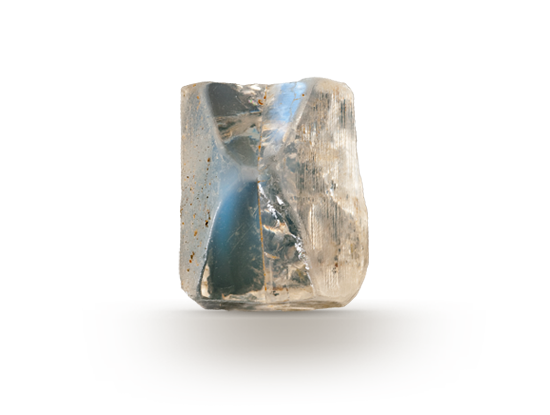
Moonstone is a variety of the feldspar-group mineral orthoclase. During formation, orthoclase and albite separate into alternating layers. When light falls between these thin layers it is scattered producing the phenomenon called adularescence. Adularescence is the light that appears to billow across a gem. Other feldspar minerals can also show adularescence including labradorite and sanidine.
Birthstones & Anniversaries
Moonstone is a birthstone for June, along with pearl and alexandrite.
Adularescence
Moonstone’s unearthly glow is caused by light scattering between microscopic layers of feldspar.
60%
The minerals in the feldspar family make up more than half of the Earth’s rocky crust.
0.5 Microns
Feldspar layers that create moonstone’s sheen are similar to the size of a wavelength of light.
Facts
-
Mineral:
Feldspar
-
Chemistry:
KAlSi3O8
-
Color:
Colorless to White, Gray, Green, Peach, Brown
-
Refractive index:
1.518 to 1.526
-
Birefringence:
0.05 to 0.008
-
Specific gravity:
2.58
- Mohs Hardness: 6.0 to 6.5
Treatments
There are a number of processes used to alter the color, apparent clarity, or improve the durability of gems.
Learn MoreSynthetics
Some gemstones have synthetic counterparts that have essentially the same chemical, physical, and optical properties, but are grown by man in a laboratory.
Learn MoreImitations
Any gem can be imitated—sometimes by manmade materials or by natural materials chosen by man to impersonate a particular gem.
Learn More
Why We Love This Gemstone
Rarity
Rare in top qualities, this ethereal gem derives from one of the earth's most common minerals.
Adularescence
Stacked layers of orthoclase and albite diffract light, creating moonstone’s adularescence.
Another Phenomena
Besides adularescence, moonstone sometimes also shows a cat’s-eye effect.
Quality Factors
An assessment of the following characteristics determines moonstone’s value.
Color

The finest moonstone is a gem of glassy purity with a mobile, electric blue shimmer.
Clarity

Characteristic inclusions include tiny tension cracks called centipedes.
Cut

As it displays moonstone’s phenomena to best advantage, cabochon is the common cut.
Carat Weight

Moonstone comes in a wide range of sizes and carat weights.
Moonstone Quality Factors: The Comprehensive Guide
Research
Explore sources, gemological research, and the role of gems in history.
Imitation Rainbow Moonstone Assemblage
Amy Cooper, Nathan Renfro, and Tara Allen , Oct 17, 2013 Read Article
Infrared Spectroscopic Study of Filled Moonstone
Li Jianjun, Weng Xiaofan, Yu Xiaoyan, Liu Xiaowei, Chen Zhenyu and Li Guihua Read ArticleRecommended Reading

Feldspar Minerals: Crystal Structures, Physical, Chemical and Microtextural Properties
Joseph V. Smith and William L. Brown